VPC Flow Logs
VPC Flow Logs enable you to capture information about the IP traffic going to and from network interfaces in your VPC.
You can create a log ingestion into Amazon OpenSearch Service either by using the Centralized Logging with OpenSearch console or by deploying a standalone CloudFormation stack.
Important
- Centralized Logging with OpenSearch supports VPCs who publish the flow log data to an Amazon S3 bucket or a CloudWatch log group. When publishing to S3, The S3 Bucket region must be the same as the Centralized Logging with OpenSearch solution region.
- The Amazon OpenSearch Service index is rotated on a daily basis by default, and you can adjust the index in the Additional Settings.
Create log ingestion (OpenSearch Engine)
Using the Centralized Logging with OpenSearch Console
- Sign in to the Centralized Logging with OpenSearch Console.
- In the navigation pane, under Log Analytics Pipelines, choose Service Log.
- Choose the Create a log ingestion button.
- In the AWS Services section, choose VPC Flow Logs.
- Choose Next.
- Under Specify settings, choose Automatic or Manual for VPC Flow Log enabling. The automatic mode will enable the VPC Flow Log and save the logs to a centralized S3 bucket if logging is not enabled yet.
- For Automatic mode, choose the VPC from the dropdown list.
- For Manual mode, enter the VPC Name and VPC Flow Logs location.
- (Optional) If you are ingesting VPC Flow logs from another account, select a linked account from the Account dropdown list first.
- Under Log Source, select S3 or CloudWatch as the source.
- Choose Next.
- In the Specify OpenSearch domain section, select an imported domain for Amazon OpenSearch domain.
- Choose Yes for Sample dashboard if you want to ingest an associated built-in Amazon OpenSearch Service dashboard.
- You can change the Index Prefix of the target Amazon OpenSearch Service index if needed. The default prefix is your VPC name.
- In the Log Lifecycle section, enter the number of days to manage the Amazon OpenSearch Service index lifecycle. The Centralized Logging with OpenSearch will create the associated Index State Management (ISM) policy automatically for this pipeline.
- In the Select log processor section, please choose the log processor.
- Choose Next.
- Add tags if needed.
- Choose Create.
Using the CloudFormation Stack
This automated AWS CloudFormation template deploys the Centralized Logging with OpenSearch - VPC Flow Logs Ingestion solution in the AWS Cloud.
| Launch in AWS Console | Download Template | |
|---|---|---|
| AWS Standard Regions |  |
Template |
| AWS China Regions |  |
Template |
-
Log in to the AWS Management Console and select above button to launch the AWS CloudFormation template. You can also download the template as a starting point for your own implementation.
-
To launch the stack in a different AWS Region, use the Region selector in the console navigation bar.
-
On the Create stack page, verify that the correct template URL shows in the Amazon S3 URL text box and choose Next.
-
On the Specify stack details page, assign a name to your solution stack.
-
Under Parameters, review the parameters for the template and modify them as necessary. This solution uses the following parameters.
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Log Bucket Name | <Requires input> |
The S3 bucket name which stores the logs. |
| Log Bucket Prefix | <Requires input> |
The S3 bucket path prefix which stores the logs. |
| Log Source Account ID | <Optional> |
The AWS Account ID of the S3 bucket. Required for cross-account log ingestion (Please add a member account first). By default, the Account ID you logged in at Step 1 will be used. |
| Log Source Region | <Optional> |
The AWS Region of the S3 bucket. By default, the Region you selected at Step 2 will be used. |
| Log Source Account Assume Role | <Optional> |
The IAM Role ARN used for cross-account log ingestion. Required for cross-account log ingestion (Please add a member account first). |
| KMS-CMK ARN | <Optional> |
The KMS-CMK ARN for encryption. Leave it blank to create a new KMS CMK. |
| Enable OpenSearch Ingestion as processor | <Optional> |
Ingestion table Arn. Leave empty if you do not use OSI as Processor. |
| S3 Backup Bucket | <Requires input> |
The S3 backup bucket name to store the failed ingestion logs. |
| Engine Type | OpenSearch | The engine type of the OpenSearch. Select OpenSearch or Elasticsearch. |
| OpenSearch Domain Name | <Requires input> |
The domain name of the Amazon OpenSearch cluster. |
| OpenSearch Endpoint | <Requires input> |
The OpenSearch endpoint URL. For example, vpc-your_opensearch_domain_name-xcvgw6uu2o6zafsiefxubwuohe.us-east-1.es.amazonaws.com |
| Index Prefix | <Requires input> |
The common prefix of OpenSearch index for the log. The index name will be <Index Prefix>-<Log Type>-<Other Suffix>. |
| Create Sample Dashboard | Yes | Whether to create a sample OpenSearch dashboard. |
| VPC ID | <Requires input> |
Select a VPC which has access to the OpenSearch domain. The log processing Lambda will reside in the selected VPC. |
| Subnet IDs | <Requires input> |
Select at least two subnets which have access to the OpenSearch domain. The log processing Lambda will reside in the subnets. Make sure the subnets have access to the Amazon S3 service. |
| Security Group ID | <Requires input> |
Select a Security Group which will be associated with the log processing Lambda. Make sure the Security Group has access to the OpenSearch domain. |
| Number Of Shards | 5 | Number of shards to distribute the index evenly across all data nodes. Keep the size of each shard between 10-50 GB. |
| Number of Replicas | 1 | Number of replicas for OpenSearch Index. Each replica is a full copy of an index. If the OpenSearch option is set to Domain with standby, you need to configure it to 2. |
| Age to Warm Storage | <Optional> |
The age required to move the index into warm storage (e.g. 7d). Index age is the time between its creation and the present. Supported units are d (days) and h (hours). This is only effective when warm storage is enabled in OpenSearch. |
| Age to Cold Storage | <Optional> |
The age required to move the index into cold storage (e.g. 30d). Index age is the time between its creation and the present. Supported units are d (days) and h (hours). This is only effective when cold storage is enabled in OpenSearch. |
| Age to Retain | <Optional> |
The age to retain the index (e.g. 180d). Index age is the time between its creation and the present. Supported units are d (days) and h (hours). If value is "", the index will not be deleted. |
| Rollover Index Size | <Optional> |
The minimum size of the shard storage required to roll over the index (e.g. 30GB). |
| Index Suffix | yyyy-MM-dd | The common suffix format of OpenSearch index for the log(Example: yyyy-MM-dd, yyyy-MM-dd-HH). The index name will be <Index Prefix>-<Log Type>-<Index Suffix>-000001. |
| Compression type | best_compression | The compression type to use to compress stored data. Available values are best_compression and default. |
| Refresh Interval | 1s | How often the index should refresh, which publishes its most recent changes and makes them available for searching. Can be set to -1 to disable refreshing. Default is 1s. |
| EnableS3Notification | True | An option to enable or disable notifications for Amazon S3 buckets. The default option is recommended for most cases. |
| LogProcessorRoleName | <Optional> |
Specify a role name for the log processor. The name should NOT duplicate an existing role name. If no name is specified, a random name is generated. |
| QueueName | <Optional> |
Specify a queue name for an SQS. The name should NOT duplicate an existing queue name. If no name is given, a random name will be generated. |
-
Choose Next.
-
On the Configure stack options page, choose Next.
-
On the Review page, review and confirm the settings. Check the box acknowledging that the template creates AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) resources.
-
Choose Create stack to deploy the stack.
You can view the status of the stack in the AWS CloudFormation console in the Status column. You should receive a CREATE_COMPLETE status in approximately 10 minutes.
View dashboard
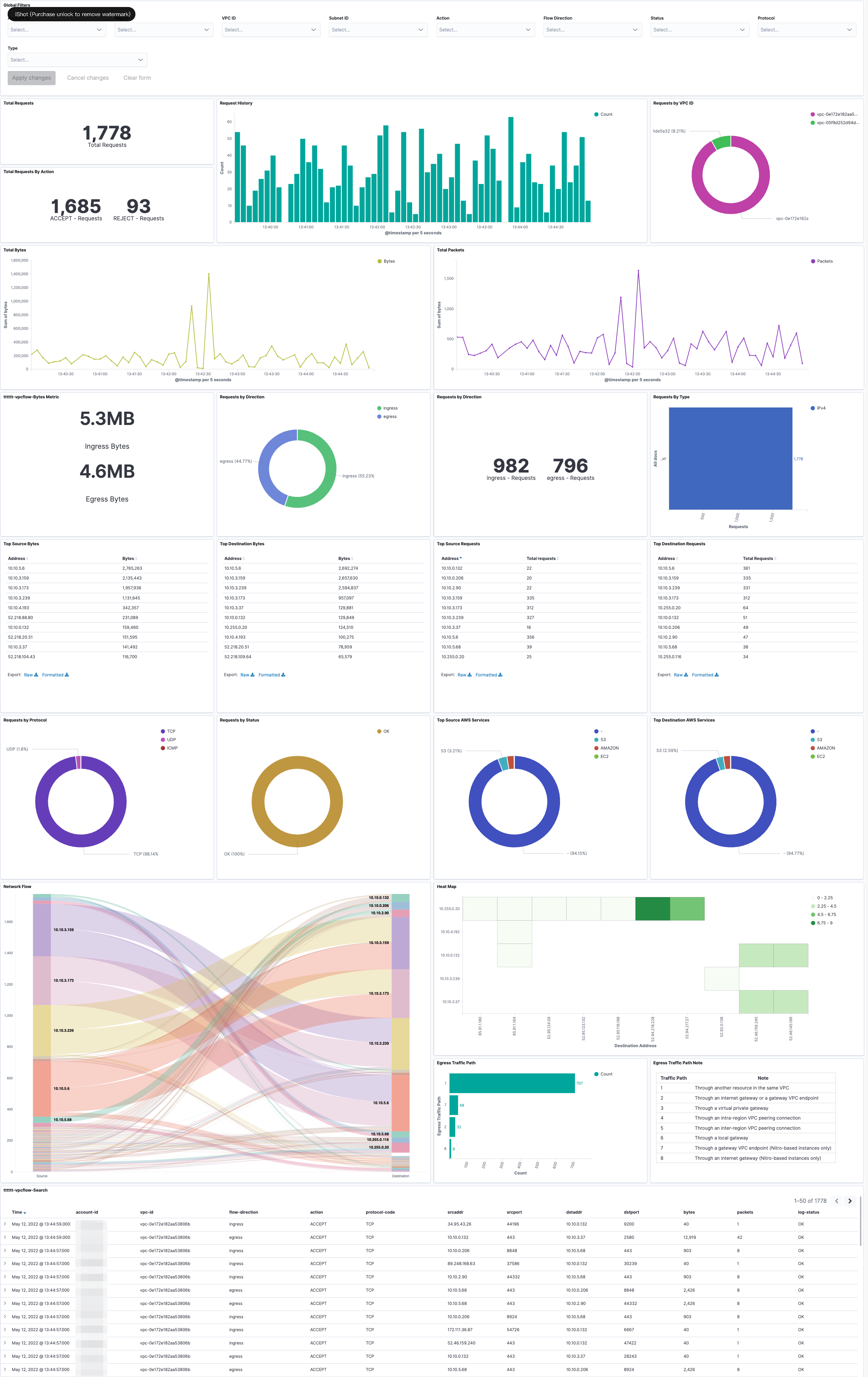
The dashboard includes the following visualizations.
| Visualization Name | Source Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Global Filters |
|
The charts are filtered according to Account ID, Region, VPC ID and other conditions. |
| Total Requests |
|
Shows the total number of network requests logged by VPC Flow Logs during a selected time period. |
| Request History |
|
Presents a bar chart that displays the distribution of events over time. |
| Requests by VPC ID |
|
Displays the proportional breakdown of network requests by source VPC using a pie chart. |
| Total Requests By Action |
|
Displays the total volume of requests segmented by action over time. |
| Total Bytes |
|
Provides visibility into overall bandwidth usage and traffic patterns across the monitored VPCs, subnets, network interfaces and security groups. |
| Total Packets |
|
Displays total logged packets over time to visualize trends, surges and dips. |
| Bytes Metric |
|
Shows the distribution of incoming (Ingress) and outgoing (Egress) network traffic volumes in bytes across the range of flows logged by VPC Flow Logs over a time period. |
| Requests By Direction |
|
Provides visibility into the proportional composition of incoming versus outgoing requests. |
| Requests By Direction |
|
Displays the total number of network flows logged by VPC Flow Logs segmented by traffic direction - Ingress vs Egress. |
| Requests By Type |
|
Shows the volume of flows for each type. This provides visibility into the protocol composition of network requests traversing the environment. |
| Top Source Bytes |
|
Displays the source IP addresses transmitting the highest outbound volume of data during the selected time period. |
| Top Destination Bytes |
|
Enables you to monitor and analyze outbound traffic from your VPC to external destinations. |
| Top Source Requests |
|
Allows you to see which resources inside your VPC are initiating external requests. |
| Top Destination Requests |
|
Allows you to see which external hosts are being contacted most by your VPC resources. |
| Requests by Protocol |
|
Displays network flows logged by VPC Flow Logs segmented by traffic type - TCP, UDP, ICMP etc. |
| Requests by Status |
|
Provides a breakdown of network flows by their traffic status - Accepted, Rejected or Other. |
| Top Source AWS Services |
|
Show the proportional distribution of flows originating from top AWS sources like S3, CloudFront, Lambda, etc. during the selected time period. |
| Top Destination AWS Services |
|
Provide visibility into IP traffic going to and from AWS services located outside your VPC. By enabling flow logs on VPC subnets/interfaces and filtering on traffic with an ACCEPT action, you can view outbound flows from your VPC to various AWS services. |
| Network Flow |
|
Allows you to view information about the IP traffic going to and from network interfaces in your VPC. |
| Heat Map |
|
Offers a visual summary of connections between source and destination IPs in your flow log data. |
| Egress Traffic Path |
|
Allows you to enable flow logging on VPC network interfaces to capture information about all IP traffic going to and from that interface. |
| Search |
|
Searching through the detailed flow log data allows pinpoint analysis of traffic around security events, network issues, changes in usage patterns, and more. |
Sample Dashboard
You can access the built-in dashboard in Amazon OpenSearch to view log data. For more information, see Access Dashboard.
You can click the below image to view the high-resolution sample dashboard.
Create log ingestion (Light Engine)
Using the Console
- Sign in to the Centralized Logging with OpenSearch Console.
- In the navigation pane, under Log Analytics Pipelines, choose Service Log.
- Choose the Create a log ingestion button.
- In the AWS Services section, choose Amazon VPC Flow.
- Choose Light Engine, Choose Next.
- Under Specify settings, choose Automatic or Manual for VPC Flow logs enabling. The automatic mode will detect the VPC Flow log location automatically.
- For Automatic mode, choose the VPC Flow from the dropdown lists.
- For Standard Log, the solution will automatically detect the log location if logging is enabled.
- For Manual mode, enter the VPC Flow ID and VPC Flow Log location.
- (Optional) If you are ingesting VpcFlow logs from another account, select a linked account from the Account dropdown list first.
- Choose Next.
- In the Specify Light Engine Configuration section, if you want to ingest associated templated Grafana dashboards, select Yes for the sample dashboard.
- You can choose an existing Grafana, or if you need to import a new one, you can go to Grafana for configuration.
- Select an S3 bucket to store partitioned logs and define a name for the log table. We have provided a predefined table name, but you can modify it according to your business needs.
- The log processing frequency is set to 5 minutes by default, with a minimum processing frequency of 1 minute.
- In the Log Lifecycle section, enter the log merge time and log archive time. We have provided default values, but you can adjust them based on your business requirements.
- Select Next.
- If desired, add tags.
- Select Create.
Using the CloudFormation Stack
This automated AWS CloudFormation template deploys the Centralized Logging with OpenSearch - VpcFlow Standard Log Ingestion template in the AWS Cloud.
| Launch in AWS Console | Download Template | |
|---|---|---|
| AWS Regions |  |
Template |
| AWS China Regions |  |
Template |
-
Log in to the AWS Management Console and select the button to launch the AWS CloudFormation template. You can also download the template as a starting point for your own implementation.
-
To launch the stack in a different AWS Region, use the Region selector in the console navigation bar.
-
On the Create stack page, verify that the correct template URL shows in the Amazon S3 URL text box and choose Next.
-
On the Specify stack details page, assign a name to your solution stack.
-
Under Parameters, review the parameters for the template and modify them as necessary. This solution uses the following parameters.
- Parameters for Pipeline settings
Parameter Default Description Pipeline Id <Requires input>The unique identifier for the pipeline is essential if you need to create multiple ALB pipelines and write different ALB logs into separate tables. To ensure uniqueness, you can generate a unique pipeline identifier using uuidgenerator. Staging Bucket Prefix AWSLogs/VpcFlowLogs The storage directory for logs in the temporary storage area should ensure the uniqueness and non-overlapping of the Prefix for different pipelines. - Parameters for Destination settings
Parameters Default Description Centralized Bucket Name <Requires input>Centralized s3 bucket name. For example, centralized-logging-bucket. Centralized Bucket Prefix datalake Centralized bucket prefix. By default, the data base location is s3://{Centralized Bucket Name}/{Centralized Bucket Prefix}/amazon_cl_centralized. Centralized Table Name VpcFlow Table name for writing data to the centralized database. You can modify it if needed. - Parameters for Scheduler settings
Parameters Default Description LogProcessor Schedule Expression rate(5 minutes) Task scheduling expression for performing log processing, with a default value of executing the LogProcessor every 5 minutes. Configuration for reference. LogMerger Schedule Expression cron(0 1 * ? ) Task scheduling expression for performing log merging, with a default value of executing the LogMerger at 1 AM every day. Configuration for reference. LogArchive Schedule Expression cron(0 2 * ? ) Task scheduling expression for performing log archiving, with a default value of executing the LogArchive at 2 AM every day. Configuration for reference. Age to Merge 7 Small file retention days, with a default value of 7, indicates that logs older than 7 days will be merged into small files. It can be adjusted as needed. Age to Archive 30 Log retention days, with a default value of 30, indicates that data older than 30 days will be archived and deleted. It can be adjusted as needed. - Parameters for Notification settings
Parameters Default Description Notification Service SNS Notification method for alerts. If your main stack is using China, you can only choose the SNS method. If your main stack is using Global, you can choose either the SNS or SES method. Recipients <Requires Input>Alert notification: If the Notification Service is SNS, enter the SNS Topic ARN here, ensuring that you have the necessary permissions. If the Notification Service is SES, enter the email addresses separated by commas here, ensuring that the email addresses are already Verified Identities in SES. The adminEmail provided during the creation of the main stack will receive a verification email by default. - Parameters for Dashboard settings
Parameters Default Description Import Dashboards FALSE Whether to import the Dashboard into Grafana, with a default value of false. If set to true, you must provide the Grafana URL and Grafana Service Account Token.。 Grafana URL <Requires Input>Grafana access URL,for example: https://alb-72277319.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com. Grafana Service Account Token <Requires Input>Grafana Service Account Token:Service Account Token created in Grafana. -
Choose Next.
-
On the Configure stack options page, choose Next.
-
On the Review page, review and confirm the settings. Check the box acknowledging that the template creates AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) resources.
-
Choose Create stack to deploy the stack.
You can view the status of the stack in the AWS CloudFormation console in the Status column. You should receive a CREATE_COMPLETE status in approximately 10 minutes.